Beware of fake GlobalProtect VPN downloads! A new malware campaign uses SEO poisoning and spoofed websites to deliver WikiLoader malware. Primarily targeting education & transportation, it tricks users with fake installers, leading to data theft & further infections.
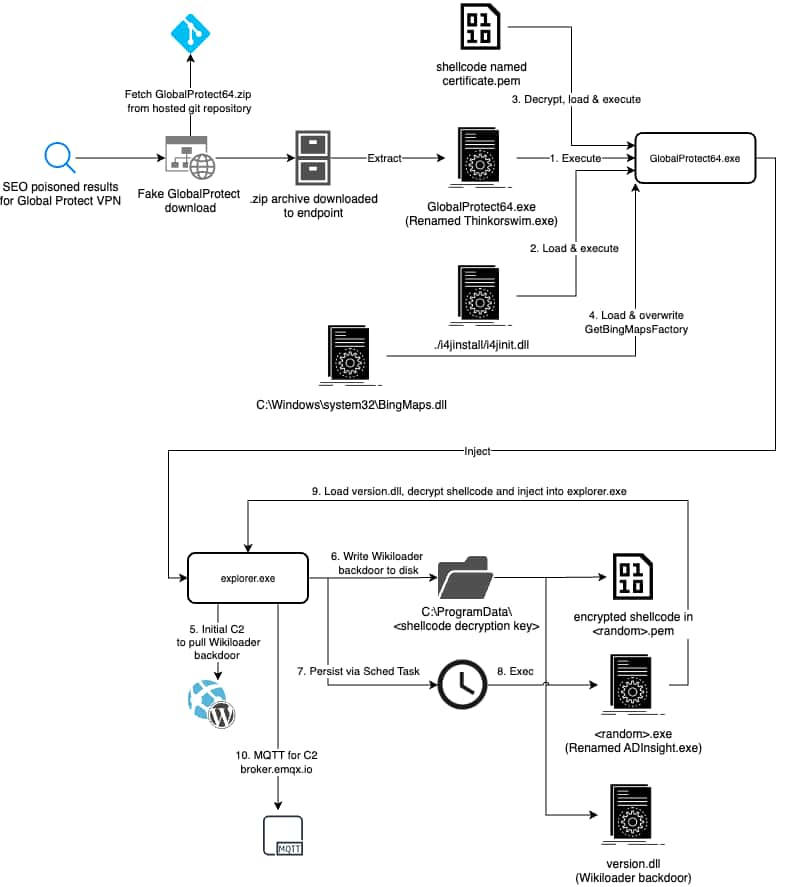
Cybersecurity researchers at Palo Alto Networks have discovered a new malware campaign that leverages Search Engine Optimization (SEO) poisoning to trick users into downloading fake GlobalProtect VPN installers. These fake installers contain a dangerous malware loader known as WikiLoader (aka WailingCrab).
WikiLoader is usually known for being rented out by cybercriminals to help them deliver other malicious programs onto victims’ computers. It was originally spread through phishing emails, but recent reports indicate that its distributors have shifted to a method called SEO poisoning.
For your information, SEO poisoning involves manipulating search engine results to make malicious websites appear high in search results. Several malware families, including ZenRAT, Zeus Panda, and SpyNote, have previously relied on this tactic to infect users by tricking them into visiting malicious sites that appear legitimate.
In this case, the attackers have created fake websites that mimic Palo Alto Networks’ GlobalProtect VPN software download pages. Unsuspecting users trying to download the VPN software may instead end up downloading WikiLoader.
WikiLoader acts as a “loader” for other malicious payloads, such as banking Trojans, which can steal sensitive information and cause further damage.
According to Palo Alto Networks’ blog post, the campaign has primarily targeted organizations in the education and transportation sectors in the United States. However, the use of SEO poisoning means that anyone searching for GlobalProtect downloads could be potentially affected.
Apart from using use legitimate-looking websites, researchers warn that the threat actors behind this campaign also used various other techniques and tools to evade detection including cloud-hosted services. WikiLoader also uses tricks like showing fake error messages and hiding malicious files inside apparently harmless programs to avoid analysis.
Palo Alto Networks has implemented measures to protect its customers from this threat through its suite of security products, including Cortex XDR and Advanced WildFire. The company has also shared detailed information about this campaign, including signs of compromise and detection rules. Organizations and individuals should review this information and take steps to protect themselves from this threat.
RELATED TOPICS
- Hackers Target Check Point VPNs, Security Fix Released
- Ivanti VPN Flaws Exploited by DSLog Backdoor and Crypto Miners
- Hackers Calling Employees to Steal VPN Credentials from US Firms
- Cisco Fixes High-Severity Code Execution and VPN Hijacking Flaws
- BlackByte Ransomware Exploits VMware Flaw in VPN-Based Attacks