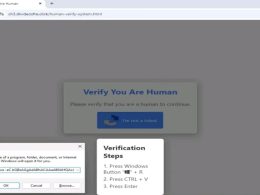
A critical vulnerability in Brave Browser allows malicious websites to appear as trusted sources during file uploads/downloads. Learn how to protect yourself and update your browser to the latest version.
A critical security vulnerability has been discovered in the popular Brave Browser, enabling malicious websites to deceive users into believing they are interacting with trusted sources. This flaw tracked as CVE-2025-23086 (classified under CWE-60), impacts desktop versions of Brave from 1.70.x to 1.73.x.
The problem lies within a feature designed to enhance user safety: displaying the origin of a website in the operating system’s file selector dialogue during file uploads or downloads. This is intended to provide a visual cue, confirming the legitimacy of the site involved in the file transfer. However, in specific scenarios, this crucial origin information was not accurately inferred, leaving a critical gap in user protection.
This misrepresentation of origin becomes particularly dangerous when combined with an “open redirect” vulnerability on a legitimate website. Open redirects mean that a trusted website lets user-controlled input redirect users to external URLs and does not validate it properly. By exploiting this combination, malicious actors can craft scenarios where a malicious website, through the open redirect, appears as a trusted source in the file selector dialogue, tricking users into interacting with it.
In May 2024, Hackread.com reported HP’s quarterly Wolf Security Threat Insights series findings, which revealed a rise in cybercriminals employing “cat-phishing” tactics, exploiting open redirect vulnerabilities and other Living-off-the-Land techniques to bypass traditional security measures
The vulnerability has a base score of 6.1, classified as Medium in severity, with an attack vector of NETWORK and low attack complexity and user interaction requirements. The consequences of this vulnerability could be drastic. Users could be unknowingly tricked into downloading malware, sharing sensitive information with malicious actors, or falling victim to sophisticated phishing attacks. This dents the core principle of user trust and security that browsers are designed to uphold.
To mitigate CVE-2025-23086, update to Brave Desktop Browser version 1.74.48 or later, check for open redirect vulnerabilities, and make sure to verify the file download sources and recognize suspicious prompts.
In addition, use security tools and browser extensions to protect against open redirects and phishing tactics. Regular updates and user awareness can significantly reduce exploitation risks. Trusted site administrators should also review their platforms to remove or fix open redirect vulnerabilities. Check out this article to learn more about how to ensure browser security.
RELATED TOPICS
- Brave browser Tor feature leaked .Onion queries to ISPs
- New Vcurms Malware Targets Popular Browsers for Data Theft
- Fake Brave browser site dropped malware, thanks to Google Ads
- New Tech Support Scam Freezes Chrome, Firefox & Brave Browser
- DOJ Proposes Breaking Up Google: Calls for Sale of Chrome Browser