Crooks pwning crooks – Hackers exploit script kiddies with XWorm RAT, compromising 18,000+ devices globally and stealing sensitive data via Telegram-based C&C.
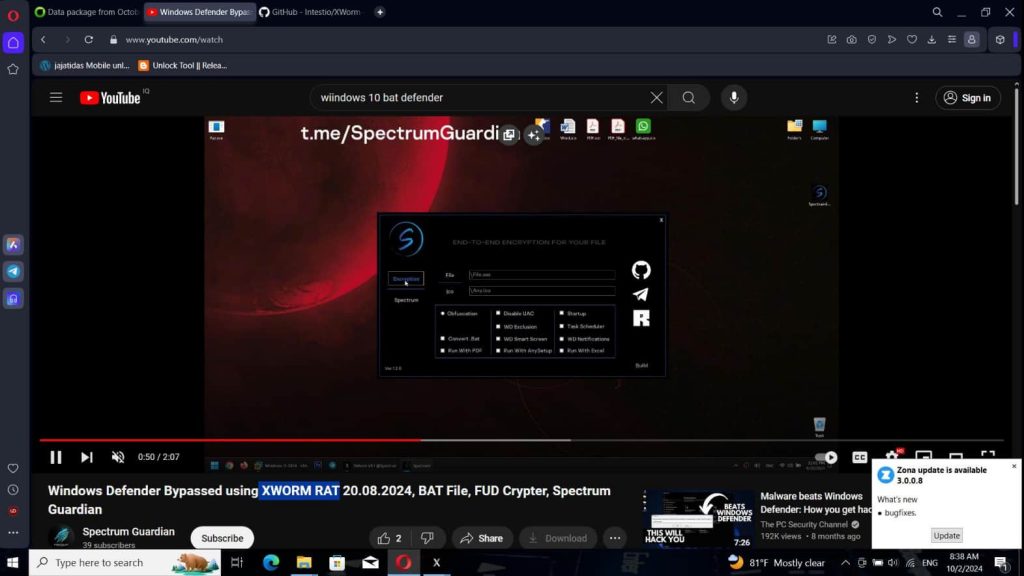
CloudSEK has discovered a new campaign involving a Trojanized version of the XWorm RAT builder. The malware spread through various channels, including file-sharing services (like Mega and Upload.ee), Github repositories (such as LifelsHex/FastCryptor and FullPenetrationTesting/888-RAT), Telegram channels (including HAX_CRYPT and inheritedeu), and even Youtube and other websites.
This campaign resulted in compromising over 18,459 devices globally. The stolen data included sensitive information like browser credentials, Discord tokens, Telegram data, and system information from the compromised devices.
“This builder provides attackers with a streamlined tool to deploy and operate a highly capable RAT, which features advanced capabilities like system reconnaissance, data exfiltration, and command execution,” CloudSEK’s blog post authored by the company’s Threat Intelligence Researcher, Vikas Kundu, revealed.
Threat actors specifically distributed a modified XWorm RAT builder to target inexperienced attackers (aka Script Kiddies). Once installed, the malware exfiltrated sensitive data like browser credentials, Discord tokens, Telegram data, and system information from the victim’s device. It also boasted advanced features like virtualization checks, the ability to modify the registry, and extensive command and control capabilities.
Furthermore, this malware relies on Telegram for its command and control functionality. It used bot tokens and Telegram API calls to receive commands from the attacker and exfiltrate stolen data.
Researchers were able to identify and leverage a “kill switch” functionality within the malware. This functionality was used to disrupt operations on active devices infected with the malware. However, this approach had limitations. Offline machines and Telegram’s rate limiting mechanisms prevented complete disruption.
Based on the investigation, researchers were able to link the threat actor to aliases “@shinyenigma” and “@milleniumrat.” Additionally, they were able to identify associated GitHub accounts and a ProtonMail address.
It is worth noting that XWorm has become a persistent threat with Ukraine’s State Service of Special Communications and Information Protection (SSSCIP) reporting its usage in Russian cyber operations against Ukraine in the first half of 2024.
To protect against such threats, organizations and individuals should use Endpoint Detection and Response (EDR) solutions to detect suspicious network activity and even malware identification.
Additionally, network monitoring using Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS) can block communication between infected devices and the malicious C&C server on Telegram. Proactive measures like blocking access to known malicious URLs and enforcing application whitelisting can prevent malware from being downloaded and executed.
RELATED ARTICLES
- P2PInfect: Self-Replicating Worm Hits Redis Instances
- FBI Warns of HiatusRAT Malware Targeting Webcams and DVRs
- Fake 7-Zip Exploit Code Traced to AI-Generated Misinterpretation
- NPM Package Disguised as an Ethereum Tool Deploys Quasar RAT
- Black Basta-Style Attack Hits Inboxes with 1,165 Emails in 90 Minutes