Python packages are being used to steal data from developers and companies. Learn about the extensive cybercriminal operation involving an Iraqi cybercrime organization and how to protect yourself from becoming a victim.
A recently uncovered cybercriminal operation targeting developers with malicious Python packages has sent shockwaves through the tech community. Detailed in a report by Checkmarx, a global leader in application security testing (AST) solutions, the intricate scheme exposes a sophisticated network of attackers leveraging the Python Package Index (PyPI), the official repository for third-party Python software, to infiltrate systems and steal sensitive data.
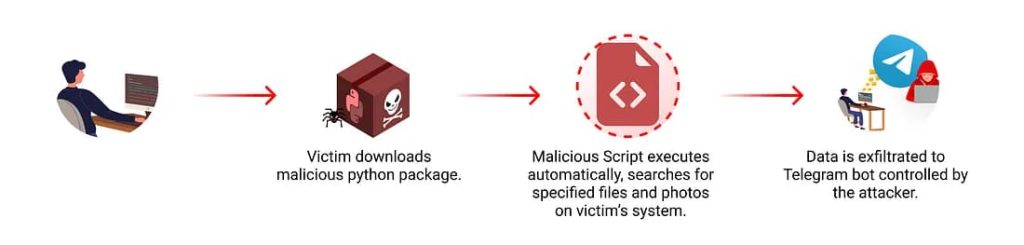
According to researchers, malicious Python packages have been uploaded to the PyPI, a popular Python repository, by a user named “dsfsdfds,” containing hidden code designed to exfiltrate data to attackers’ Telegram bot. This bot serves as their C2 center, and is potentially linked to a broader criminal network based in Iraq with operations spanning multiple countries. Here are the packages’ names:
- testbrojct2
- proxyalhttp
- proxyfullscraper
- proxyfullscrapers
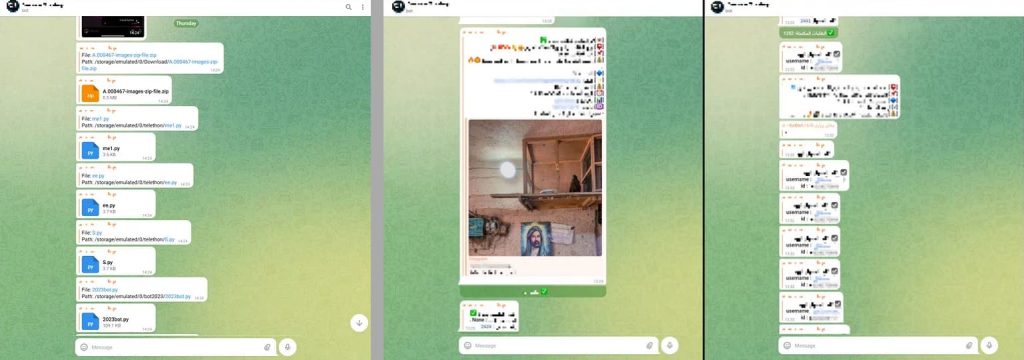
The malicious script uses a systematic approach to compromise a victim’s system and extract sensitive data. It scans the user’s file system, focusing on the root folder and DCIM folder, and searches for files with extensions like.py,.php, and.zip, and photos with.png,.jpg, and.jpeg. It sends the data to the attackers’ Telegram bot without the user’s knowledge or consent. Further probing revealed that the malicious packages contained hardcoded “chat_id” and “bot_token” allowing direct access to the attacker’s Telegram bot.
The bot had a history dating back to 2022 and contained over 90,000 messages, primarily in Arabic and originating from Iraq. It appeared to function as an underground marketplace offering illicit services, including “purchasing Telegram and Instagram views, followers, spam services, and discounted Netflix memberships” the report explained.
The bot’s message history revealed evidence of financial theft from compromised systems, “displaying evidence of success from the malicious python packages campaign” researchers concluded in their report.
Researchers believe developers and their affiliated companies are key targets of this campaign, designed to steal intellectual property and valuable assets, integrating compromised code into software used by millions worldwide.
The compromised packages can introduce vulnerabilities into software projects, potentially affecting individual developers and enterprises, highlighting the need for comprehensive security measures.
PyPI is frequently abused in supply chain attacks. In March 2024, PyPI suspended new projects and user registrations due to malicious packages. In January 2024, FortiGuard Labs exposed a crypto-stealing PyPI malware targeting Windows and Linux users.
The latest discovery highlights the need for enhanced security measures in package repositories, urging organizations to implement strict practices like code signing, vulnerability scanning, and verifying software source authenticity.