Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a sub-domain in the Artificial Intelligence (AI) world that aims to understand and interpret naturalistic language use through computers. It is a vast domain that has gained significant traction in various applications across industries such as healthcare, finance, customer service, and entertainment.
As AI continues to advance, smarter NLP models have emerged, making human-like language understanding more efficient and easier to comprehend by mimicking day-to-day conversations. Soon there will be a day when human interaction and manual interactions will be reduced and AI will take on the majority of the operational burden.
There are pros and cons to it – the cons being unemployment and making humans make less critical decisions and think less. This can lead to an increase in jobs like AI researchers, AI policy experts and AI product management. With the widespread knowledge available in text corpora, AI can make more efficient and experienced decisions and connect humans and machines.
This article is not about weighing the positives and negatives but focuses on how industries and businesses can incorporate AI bots and build automated systems for customer support, sentimental analysis and other GenAI benefits like RAG which stands for Retrieval-Augmented Generation, a technique used to enhance internal document understanding and lookup.
However, challenges such as significant capital investment, required compute infrastructure, data scale for training transformers, and technical expertise in deep learning workflows must be considered as important factors to automate the products/services. One such advanced AI model that is widely adopted specifically for this purpose is Large Language Models (LLMs) – they are designed to process and produce human-like text using extensive amounts of textual corpora.
How do LLMs Work?
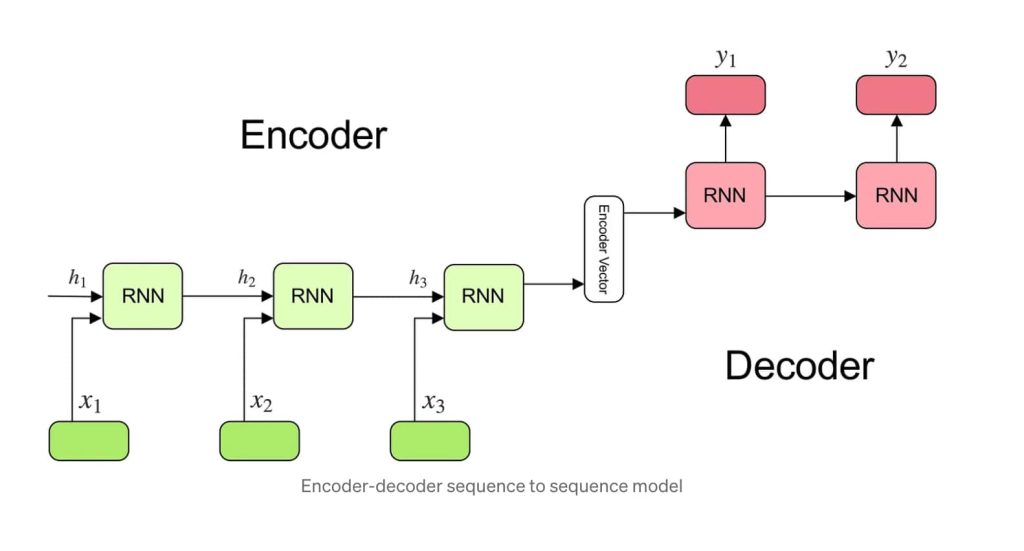
LLMs are trained using vast quantities of text data, enabling them to generate internal models of language. The size of the data used to train LLMs is in petabytes, with one-petabyte equivalent to one million gigabytes. This data can include books, research papers, articles, speeches, and more. Transformers, a type of neural network architecture, help read back and forth the sequential lines of data or code, allowing for an understanding of the semantics and context of each word in a sentence.
This capability enables transformers to predict words in a sentence or provide accurate responses to questions based on previously seen data. Transformers are categorized into different classes suitable for various use cases: Encoder-only models like BERT excel at understanding the text, making them suitable for tasks such as classifying information or determining sentiment.
Conversely, decoder-only models like GPT-3 specialize in generating text and producing content like articles or scripts. Finally, encoder-decoder models, exemplified by T5, combine both functionalities, making them ideal for tasks that involve understanding input text and generating output text, such as summarizing articles.
Encoder-only models, like BERT and RoBERTa, function as expert text analysts, ideal for tasks such as grammar correction, email organization, and content summarization. On the other hand, decoder-only models, such as GPT-3, are skilled wordsmiths who excel at creating interesting articles, persuasive text content, and video scripts.
Combining these features, encoder-decoder models such as T5 function as versatile translators and summarizers, capable of both reading and creating text, making them invaluable across various applications, including e-commerce to human resources and beyond.
Large PhraseologyModels (LLMs) in Business Domains
LLMs are utilized in various business domains to reduce operation burden, improve customer experiences, and drive innovation. LLMs are revolutionizing customer services and support by providing virtual assistants that can handle an immense amount of customer queries, help in troubleshooting issues and provide 24/7 assistance.
Some day-to-day examples, where people use chatbots, are to troubleshoot issues in the router when wifi is down, they also use it to reset passwords or get information about products. Chat bots support multiple languages catering to people across various regions. The famous bots that you might have used recently could include – IBM Watson, ChatGPT or SalesForce Einstein.
LLMs are extensively utilized for sentiment analysis to understand the tone or the sentiments of users behind the text, for example, if the user comments on a product – “The footwear is amazing!” – footwear and amazing are tokens that point to the user’s positive outlook on the item.
The LLMs can accurately classify the positive and negative comments for analysis which can be used to make critical business decisions for revenue growth. BERT, GPT-3 and RoBERTa are transformers that have been supporting the analysis for a very long period.
Other use cases of LLMs include – creating content like blogs, articles, Ad content and stories for businesses. It is robustly used in e-commerce for personalized product recommendations and improving the ranking of products. Other benefits range from Youtubers can create scripts for their video content and students can use the services to create academic content.
Human resource organizations use LLM models for resume screening in a fraction of a second, review tax documents, summarize job descriptions and create notes during interviews. Employee onboarding processes have become easier and streamlined as LLMs have guided new employees through the onboarding process, answering their questions and providing necessary information.
Several prominent Large Language Models (LLMs) have emerged, including the GPT series developed by OpenAI, Google’s Gemini, Anthropic’s Claude, and Microsoft’s Turing-NLG.
LLM offerings in Cloud Computing Platforms
Amazon Bedrock:
Amazon Bedrock is widely used for content creation in marketing and advertising. Bedrock agents can create campaigns, social media posts, and newspaper articles. It offers access to various powerful foundation models from AI startups like AI21 Labs, Anthropic, and Stability AI, as well as Amazon’s own Titan models. Bedrock provides APIs for integrating generative AI capabilities into applications without extensive AI expertise, handling infrastructure, model hosting, and scaling. The users get an opportunity to choose among the models or let Bedrock use its intelligence to automatically choose the appropriate foundational model to generate output content.
Google’s Vertex Gemini:
Gemini excels at understanding and generating human-like text, handling complex queries, providing detailed answers, and engaging in nuanced conversations. It has a strong contextual understanding, maintaining coherent and relevant responses over longer interactions. It is widely used in Google’s ecosystem, including Google Cloud Platform, Google Search, Google Assistant and Gmail, and Google Ads. Developers can access Vertex via Google Cloud’s Vertex AI platform.
Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services:
Azure Cognitive service is employed to create and manage chatbots and virtual assistants with advanced conversational capabilities. This service is suitable for enterprises that heavily use Microsoft products. Azure Cognitive services can be availed by creating an Azure account and creating a resource for Cognitive service and then you can use the offered APIs for vision, speech, language and decision. Various languages like – java, python, C# and Javascript can be used to call these APIs.
Comparison of LLM Services in Cloud Computing Platforms
Each service has its strengths and is tailored to different needs. Google’s Vertex AI offers cutting-edge technology and is widely used within Google’s ecosystem, providing customers the capability to develop custom models that can be beneficial for highly complex projects.
Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services delivers reliable, scalable solutions with enterprise-grade support, making it particularly useful for those already integrated into the Microsoft ecosystem. Amazon Bedrock offers a variety of model choices and seamless AWS integration, supporting rapid development, text generation, and code completion, as well as image editing and creation.
Takeaway
Natural Language Processing (NLP) and Large Language Models (LLMs) are pivotal in transforming how businesses operate and interact with customers. By leveraging advanced models like GPT, Gemini, Claude, and Turing-NLG, organizations can enhance customer support, conduct sentiment analysis, and automate content creation, leading to more efficient operations and improved decision-making.
Cloud computing platforms such as Amazon Bedrock, Google Vertex Gemini, and Microsoft Azure Cognitive Services offer tailored solutions that further empower businesses with cutting-edge AI capabilities, each bringing unique strengths to meet various needs.
As AI technology continues to evolve, businesses that harness these tools effectively will gain a significant competitive edge, driving innovation and improving overall performance.
References
- https://arxiv.org/abs/2204.02311
- https://aws.amazon.com/bedrock/
- https://openai.com/index/openai-api/
- https://techcommunity.microsoft.com/
- https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5sLYAQS9sWQ&t=271s
- https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/ai-services/openai/
- https://www.nvidia.com/en-us/glossary/large-language-models/
- https://medium.com/@kaushikvikas/amazon-bedrock-vs-8a58059026da
- https://www.turing.com/kb/brief-introduction-to-transformers-and-their-power
- https://towardsdatascience.com/understanding-encoder-decoder-sequence-to-sequence-model-679e04af4346
- https://deepmindlabs.ai/2023/11/unlocking-the-power-of-natural-language-processing-a-gateway-to-smarter-solutions/
- https://www.future-processing.com/blog/how-is-natural-language-processing-nlp-used-in-business/
- https://dev.to/sahilmadhyan/unlocking-the-power-of-large-language-models-in-ai-185p