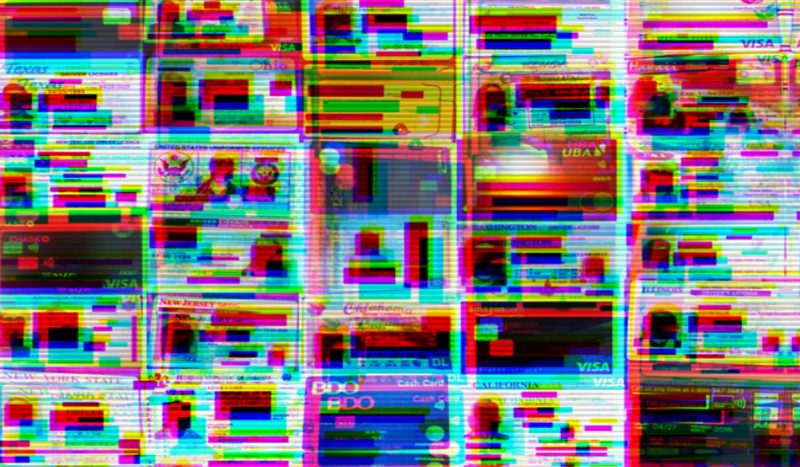
The staggering 198.3 gigabytes of misconfigured database contained more than 260,000 records including customer selfies with unredacted credit cards.
Cybersecurity researcher Jeremiah Fowler recently uncovered a misconfigured cloud database that had left a wealth of sensitive data exposed. The affected database contained records attributed to customers of BuyGoods.com, alternatively recognized in the industry as Softwareproject.
For your information, in their own words, “BuyGoods.com is a global ecommerce marketplace and business management platform for product owners, marketers, and online shoppers.” Hailing from Wilmington, Delaware BuyGoods.com boasts a user base of 3 million consumers spanning across 17 countries.
What data was leaked?
The exposed database, totalling 198.3 gigabytes in size, lacked any form of security authentication, being openly accessible to the public. Within this unprotected database were more than 260,000 records, containing a comprehensive range of information. This included details regarding affiliate payouts, refund transactions, invoices, accounting records, and various other forms of data.
What’s worse, the exposed server also laid bare the personal records of customers and affiliates, containing highly sensitive Personally Identifiable Information (PII) and Know Your Customer (KYC) data.
This exposed information included customers’ selfies alongside their personal identification cards, licenses, passports, and even unredacted credit card details. The global impact of this privacy breach could have been substantial, as these records spanned individuals from various parts of the world.
In a blog post for WebsitePlanet, Fowler disclosed that he promptly notified BuyGoods.com about the security issue. Despite the company’s swift acknowledgement and assurance that the data had been secured, Fowler discovered that the server remained exposed days after his responsible disclosure.
“I immediately sent a responsible disclosure notice and received the following message via e-mail: “Thank you for letting us know about this. The access issue to the directories list has now been resolved. We are moving all PII data away from those public buckets”. Despite efforts to resolve the issue, it appeared that the database was still accessible for some time before being restricted,” Fowler explained.

Potential Threats
Misconfigured servers carrying PII or KYC data pose a massive threat to the online privacy and physical security of unsuspected customers. What some may label as a simple data leak can become a nightmare.
In the wrong hands, this sensitive information can fuel identity theft, leading to financial fraud and unauthorized access to personal accounts. Moreover, criminals may exploit the stolen data for malicious activities, creating fake profiles, and jeopardizing security and public safety.
The aftermath of such a breach could result in widespread chaos, compromising the trust individuals place in digital systems and the protection of their most private information.
Securing a Misconfigured Database
Admins can take several measures to address the issue of misconfigured databases or servers. Here are some of the key steps that should be vital in database security and protection:
- Regular Audits and Assessments:
Conduct regular audits and assessments of database configurations to identify vulnerabilities and misconfigurations. This proactive approach helps in detecting issues before they can be exploited by malicious actors. - Implement Least Privilege Principle:
Limit user access rights to the minimum necessary for their roles. Applying the principle of least privilege reduces the potential impact of a security breach by restricting unauthorized access to sensitive data. - Use Strong Authentication and Access Controls:
Enforce strong authentication mechanisms, such as multi-factor authentication, to enhance the security of access credentials. Additionally, implement robust access controls to ensure that only authorized individuals can make changes to the database configurations. - Encrypt Sensitive Data:
Encrypt sensitive data both at rest and in transit. This adds an extra layer of protection, making it harder for unauthorized users to extract meaningful information even if they gain access to the database. - Regularly Update and Patch Systems:
Keep database systems and server software up to date with the latest security patches. Regular updates help to address known vulnerabilities and enhance the overall security posture of the system. - Monitor and Log Activities:
Implement comprehensive monitoring and logging mechanisms to detect unusual activities or unauthorized access promptly. Monitoring tools can help admins identify potential security incidents and respond swiftly. - Educate Personnel:
Train and educate administrators and other personnel about the importance of proper configuration practices and the potential risks associated with misconfigurations. Creating awareness can contribute to a culture of security within the organization. - Automated Configuration Management:
Utilize automated configuration management tools to ensure consistency and accuracy in server configurations. Automation reduces the likelihood of human error and helps maintain a secure and standardized environment. - Incident Response Plan:
Develop and regularly update an incident response plan to guide admins in the event of a security incident. This plan should include steps to investigate, contain, eradicate, and recover from a misconfiguration-related breach. - Engage External Security Auditors:
Periodically engage external security experts to conduct thorough assessments and penetration testing. External audits provide an unbiased perspective and can uncover vulnerabilities that may be overlooked internally.
RELATED ARTICLES
- Call Center Provider Experiences Major Data Leak
- FOX News Exposed 13 Million Sensitive Records Online
- Cosmetic giant Estée Lauder exposed 440 million records online
- Z2U Market Leak Exposes Access to Illicit Services and Malware
- Texas School Safety Software Data Leak Endangers Student Safety
- “Biggest webmaster forum” Digital Point exposes trove of user data