StormBamboo abuses insecure software updates! Don’t be a victim! This article explores how the StormBamboo group compromises ISPs to tamper with software update mechanisms and deploy malware.
Threat intelligence firm Volexity has revealed that a Chinese threat actor is using ISP-level DNS poisoning to deliver malware against its targets. During an investigation started in mid-2023, Volexity discovered the actor is targeting software vendors exploiting insecure update workflows to spread malware.
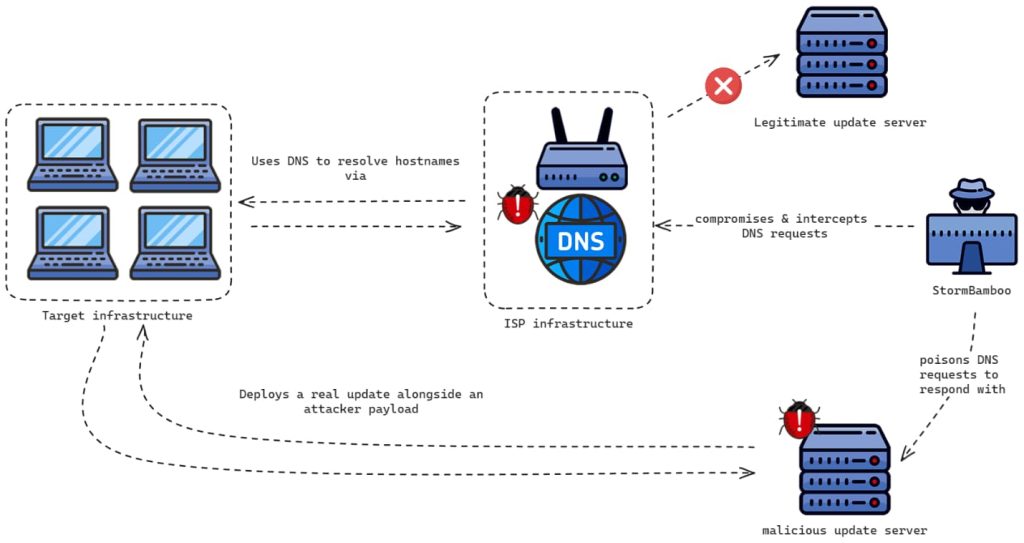
The APT actor tracked as StormBamboo (also known as Evasive Panda, Bronze Highland, Daggerfly, and StormCloud, is notorious for cyberespionage operations targeting Asian organizations. The group has mastered the art of exploiting third parties like ISPs to launch follow-on attacks. Their latest scheme involves manipulating insecure software update mechanisms to silently inject malware onto unsuspecting victim machines.
Volexity’s blog post revealed its researchers discovered StormBamboo was altering DNS query responses for domains linked to automatic software update mechanisms. The attackers targeted software using insecure update mechanisms like HTTP and failed to validate the installers’ digital signatures, leading to malware installation instead of intended updates.
The attack hinges on a technique known as man-in-the-middle (MITM), where the attackers essentially position themselves between a targeted device and a trusted server. This allows them to intercept and manipulate communication flowing between the two parties.
In the case of the ISP compromise, the attackers were able to poison DNS requests, a critical function that translates website addresses into numerical IP addresses. By tampering with DNS responses, the attackers could redirect users to malicious websites designed to steal sensitive information.
Attackers used information-stealing malware, including MgBot and Pocostick, for Windows machines and Macma for MacOS devices. MgBot, used by Evasive Panda for over a decade, was found against China’s Tibetan population earlier this year. In the 2023 attacks Volexity analyzed, certain apps requested updates and instead installed MgBot and Macma.
MgBot aka Pocostick is a particularly nasty piece of software that employs a range of stealthy techniques to evade detection and harvest sensitive data from compromised systems.
Additionally, StormBamboo has been observed deploying a malicious browser extension named RELOADEXT, likely designed to manipulate search results or inject advertisements into web browsing sessions.
The ISP, upon discovering the compromise, took swift action to mitigate the damage with help from Volexity. Key network devices were rebooted, effectively disrupting the attackers’ MitM operation. However, the attackers had already exploited the disruption to deploy information-stealing malware onto unsuspecting devices.
“As the ISP rebooted and took various components of the network offline, the DNS poisoning immediately stopped. During this time, it was not possible to pinpoint a specific device that was compromised, but various components of the infrastructure were updated or left offline and the activity ceased.”
Volexity
RELATED TOPICS
- DNS Tunneling Used for Stealthy Scans and Email Tracking
- Savvy Seahorse Using Fake ChatGPT in DNS Investment Scam
- “Sitting Ducks” DNS Attack Lets Hackers Easy Domain Takeover
- DeFi Hack Alert: Squarespace Domains Vulnerable to DNS Hijacking
- Cybersecurity Firm Hacks Itself, Finds DNS Flaw Leak AWS Credentials